As a system administrator, I try to follow the principle of least privilege (minimal privilege). Therefore, in the systems I install, I block all incoming and outgoing ports by default and open only when needed.
While setting up Oracle XE on some machines, port 1521 usually needs to be open so that engineers can connect to the database on that port and perform their developmental work. If this port is blocked and only SSH port is opened in the local firewall, then SQL Developer 4.1 provides a facility to create SSH tunnel and allows connections over that secure tunnel.
Get Started
- Launching SQL Developer 4.1, click on the View > SSH menu to open up the SSH Connections panel.
- In the SSH panel, right-click on the SSH Hosts and choose New SSH Host
- Complete the SSH connections dialog –
- Name – This is the connection name and can be anything which identifies the connection.
- Host – This is the host name or IP address of the host where we are trying to establish the SSH connectivity.
- Port – This is the port on which your SSH daemon listens to. By default the port is 22, but if your SysAdmin has changed this to something else, please put that value here.
- If you use a SSH Key File to connect to the server, select the check box “Use key file” and then Browse and select the private key file which needs to be used to establish connection. In case you use password, the you can ignore this check box and during connection, you will be prompted for your password.
- In order to tunnel the Oracle connections inside an SSH tunnel, you need to select the check box “Add a Local Port Forward”. I normally leave the values in the Name, Host and Port fields to default, but you can change them. If you change these values from Default, localhost and 1521 respectively, then please note it down as you will need to specify this host name and port number in the Oracle Database connections dialog box.
- You can now right click on the SSH Host which you created and click on “Test” to test the connection.
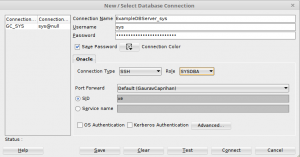
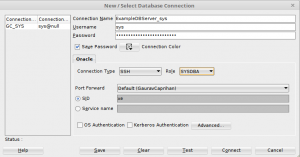
- After you see the success message, create a new connection for your Oracle database by providing your connection details as usual.
- If you select the “Connection Type” as “Basic” from the drop-down, the only change would be you host name and port number in case you changed those while creating the SSH connection.
- If you select the “Connection Type” as “SSH” from the drop down, you just select the Connection name which you created from the “Port Forward” drop down.
I hope this helps.
