A short while back, I wrote a series on Resilience, focusing on why automated recovery isn’t optional anymore. (If you missed the first post, you can find it here: [The Unseen Heroes: Why Automated System Recovery Isn’t Optional Anymore]).
The argument that human speed cannot match machine speed, is now facing its ultimate test. We are witnessing the rise of Agentic AI. Agentic AI is a new class of autonomous attacker operating at light speed, capable of learning, adapting, and executing a complete breach before human teams even fully wake up.
This evolution demands more than recovery; it requires an ironclad strategy for automated, complete infrastructure rebuild.
Autonomy That Learns and Adapts
For years, the threat landscape escalated from small hacking groups to the proliferation of the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model. RaaS democratized cybercrime, allowing moderately skilled criminals to rent sophisticated tools on the dark web for a subscription fee (learn more about the RaaS model here: What is Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)?).
The emergence of Agentic AI is the next fundamental leap.
Unlike Generative AI, which simply assists with tasks, Agentic AI is proactive, autonomous, and adaptive. These AI agents don’t follow preprogrammed scripts; they learn on the fly, tailoring their attack strategies to the specific environment they encounter.
For criminals, Agentic AI is a powerful tool because it drastically lowers the barrier to entry for sophisticated attacks. By automating complex tasks like reconnaissance and tailored phishing, these systems can orchestrate campaigns faster and more affordably than hiring large teams of human hackers, ultimately making cybercrime more accessible and attractive (Source: UC Berkeley CLTC)
Agentic ransomware represents a collection of bots that execute every step of a successful attack faster and better than human operators. The implications for recovery are profound: you are no longer fighting a team of humans, but an army of autonomous systems.
The Warning Signs Are Already Here
Recent high-profile incidents illustrate that no industry is safe, and the time-to-breach window is shrinking:
- Change Healthcare (Early 2024): This major incident demonstrated how a single point of failure can catastrophically disrupt the U.S. healthcare system, underscoring the severity of supply-chain attacks (Read incident details here).
- Snowflake & Ticketmaster (Mid-2024): A sophisticated attack that exploited stolen credentials to compromise cloud environments, leading to massive data theft and proving that third-party cloud services are not magically resilient on their own (Learn more about the Snowflake/Ticketmaster breach).
- The Rise of Non-Human Identity (NHI) Exploitation (2025): Security experts warn that 2025 is seeing a surge in attacks exploiting Non-Human Identities (API keys, service accounts). These high-privilege credentials, often poorly managed, are prime targets for autonomous AI agents seeking to move laterally without detection (Read more on 2025 NHI risks).
The Myth of Readiness in a Machine-Speed World
When faced with an attacker operating at machine velocity, relying solely on prevention-focused security creates a fragile barrier.
So, why do well-funded organizations still struggle? In many cases, the root cause lies within. Organizations are undermined by a series of internal fractures:
Siloed Teams and Fragmented Processes
When cybersecurity, cloud operations, application development and business-continuity teams function in isolation, vital information becomes trapped inside departmental silos, knowledge of application dependencies, network configurations or privileged credentials may live only in one team or one tool. Here are some examples –
- Cisco Systems’s white-paper shows how siloed NetOps and SecOps teams lead to delayed detection and containment of vulnerability-events, undermining resilience.
- An industry article highlights that when delivering a cloud-based service like Microsoft Teams, issues spread across device, network, security, service-owner and third-party teams—and when each team only worries about “is this our problem?” the root-cause is delayed.
Organizations must now –
- Integrate cross-functional teams and ensure shared ownership of outcomes.
- Map and document critical dependencies across teams (apps, networks, credentials).
- Use joint tools and run-books so knowledge isn’t locked in one group.
Runbooks That Are Theoretical, Not Executable
Policies and operational run-books often exist only in Wiki or Confluence pages. These are usually never tested end-to-end for a real-world crisis. When a disruption hits, these “prepare-on-paper” plans prove next-to-useless because they haven’t been executed, updated or validated in context. Some of the examples to illustrate this are –
- A study on cloud migration failures emphasises that most issues aren’t purely technical, but stem from poor process, obscure roles and un-tested plans.
- In the context of cloud migrations, the guidance “Top 10 Unexpected Cloud Migration Challenges” emphasises that post-migration testing and refinement are often skipped. This means that even when systems are live, recovery paths may not exist.
The path forward lies in to –
- Validate and rehears e run-books using realistic simulations, not just table-top reviews.
- Ensure that documentation is maintained in a form that can be executed (scripts, automation, playbooks) not just “slides”.
- Assign clear roles, triggers and escalation paths—every participant must know when and how they act.
Over-Reliance on Cloud Migration as a Guarantee of Resilience
Many organisations assume that migrating to the cloud automatically improves resilience. In reality, cloud migration only shifts the complexity: without fully validated rebuild paths, end-to-end environment re-provisioning and regular recovery testing, cloud-based systems can still fail under crisis.
Real-world examples brings this challenge into focus –
- A recent issue reported by Amazon Web Services (AWS) showed thousands of organisations facing outage due to a DNS error, reminding us that even “trusted” cloud platforms aren’t immune—and simply “being in the cloud” doesn’t equal resilience.
- Research shows that “1 in 3 enterprise cloud migrations fail” to meet schedule or budget expectations, partly because of weak understanding of dependencies and recovery requirements.
These underscores the importance to –
- Treat cloud migration as an opportunity to rebuild resiliency, not assume it comes for free.
- Map and test full application environment re-builds (resources, identities, configurations) under worst-case conditions.
- Conduct regular fail-over and rebuild drills; validate that recovery is end-to-end and not just infrastructure-level.
The risk is simple: The very worst time to discover a missing configuration file or an undocumented dependency is during your first attempt at a crisis rebuild.
Building Back at Machine Speed
The implications of Agentic AI are clear: you must be able to restore your entire infrastructure to a clean point-in-time state faster than the attacker can cause irreparable damage. The goal is no longer recovery (restoring data to an existing system), but a complete, automated rebuild.
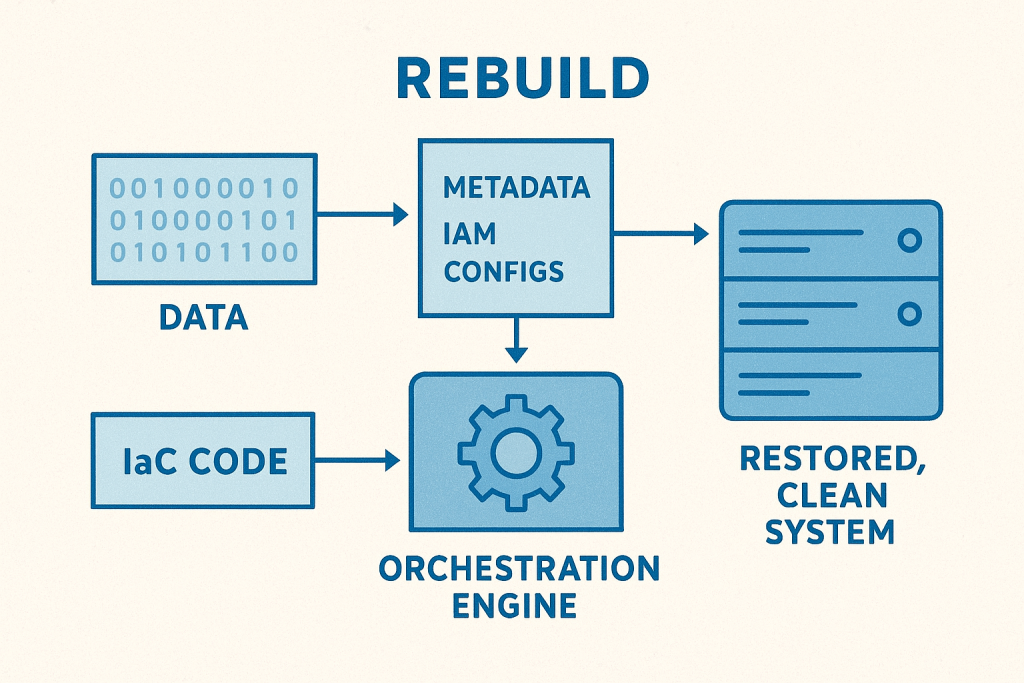
This capability rests on three pillars:
- Comprehensive Metadata Capture: Rebuilding requires capturing all relevant metadata—not just application data, but the configurations, Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, networking topologies, resource dependencies, and API endpoints. This is the complete blueprint of your operational state.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): The rebuild process must be entirely code-driven. This means integrating previously manual or fragmented recovery steps into verifiable, executable code. IaC ensures that the environment is built back exactly as intended, eliminating human error.
- Automated Orchestration and Verification: This pillar ties the first two together. The rebuild cannot be a set of sequential manual scripts; it must be a single, automated pipeline that executes the IaC, restores the data/metadata, and verifies the new environment against a known good state before handing control back to the business. This orchestration ensures the rapid, clean point-in-time restoration required.
By making your infrastructure definition and its restoration process code, you match the speed of the attack with the speed of your defense.
Resilience at the Speed of Code
Automating the full rebuild process transforms disaster recovery testing from an expensive chore into a strategic tool for cost optimization and continuous validation.
Traditional disaster recovery tests are disruptive, costly, and prone to human error. When the rebuild is fully automated:
- Validated Resilience: Testing can be executed frequently—even daily—without human intervention, providing continuous, high-confidence validation that your environment can be restored to a secure state.
- Cost Efficiency: Regular automated rebuilds act as an audit tool. If the rebuild process reveals that your production environment only requires 70% of the currently provisioned resources to run effectively, you gain immediate, actionable insight for reducing infrastructure costs.
- Simplicity and Consistency: Automated orchestration replaces complex, documented steps with verifiable, repeatable code, lowering operational complexity and the reliance on individual expertise during a high-pressure incident.
Agentic AI has closed the window for slow, manual response. Resilience now means embracing the speed of code—making your restoration capability as fast, autonomous, and adaptive as the threat itself.